
by Bruce Wells | Apr 8, 2024 | Petroleum Art
Pennsylvania oilfield tragedy led to new safety and firefighting technologies — and a work of art.
The danger involved in America’s early petroleum industry was revealed when the first commercial well went up in flames just weeks after finding oil in the summer of 1859 — becoming the first oil well fire. More serious infernos would follow as the young industry’s early technologies struggled to keep up.
While Pennsylvania oil region grew — and wooden derricks multiplied on hillsides — an 1861 deadly explosion and fire at Rouseville added urgency to the industry’s need for inventing safer ways for drilling wells.

A marker dedicated in 1996 on State Highway 8 near Rouseville by the Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission. Henry Rouse’s reputation made him a respected leader of the early oil industry.
On April 17, 1861, a highly pressurized well’s geyser of oil exploded in flames on the Buchanan Farm at Rouseville, killing the well’s owner and more than a dozen bystanders.
Sometimes called “Oil Well Fire Near Titusville” but more accurately, Rouseville, the early oilfield tragedy was overshadowed by the greater tragedy of the Civil War. Fort Sumter fell on April 13, 1861; Henry Rouse’s oil well exploded four days later.

The Little and Merrick well at Oil Creek, drilled by respected teacher and businessman Henry Rouse, unexpectedly had hit a pressurized oil and natural gas geologic formation at a depth of just 320 feet. Given the limited drilling technologies for controlling the pressure, the well’s production of 3,000 barrels of oil per day was out of control.
The Rouse Estate later reported, “A breathless worker ran up to him, telling him to ‘come quickly’ as they’d ‘hit a big one.’ According to the best accounts of the time, the ‘big one’ was the world’s first legitimate oil gusher. As oil spouted from the ground, Henry Rouse and the others stood by wondering how to control the phenomenon.”

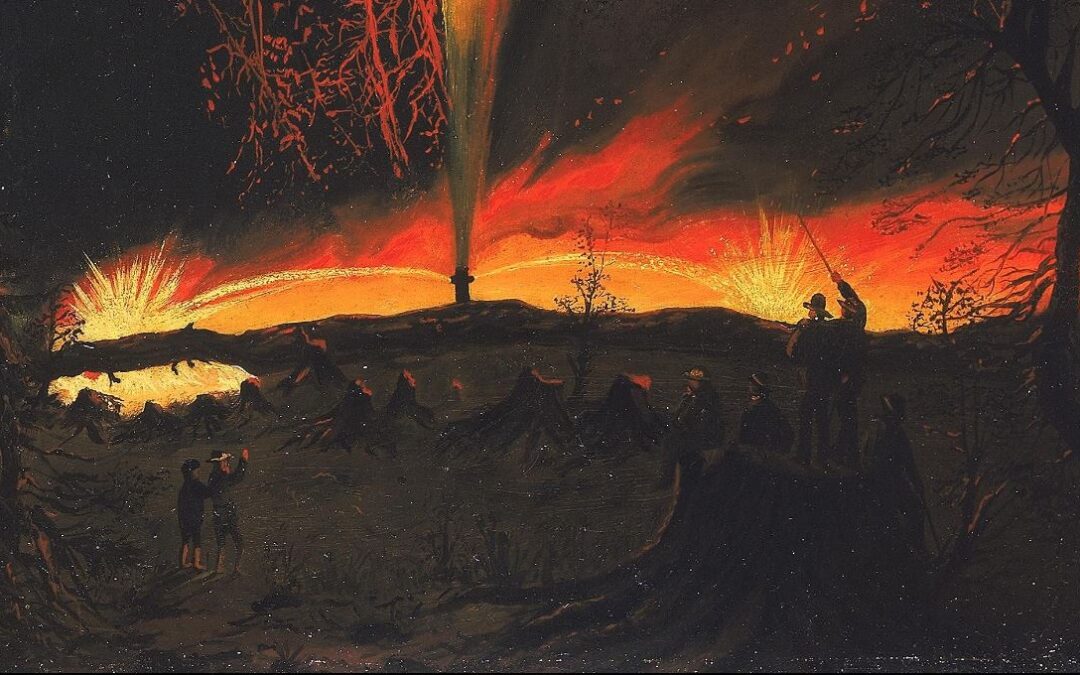
Detail from “Burning Oil Well at Night, near Rouseville, Pennsylvania,” a painting by James Hamilton of the 1861 oil well fire that killed Henry Rouse today is in the collection of the Smithsonian American Art Museum, Washington, D.C.
The towering gusher also had attracted people from town; many had become covered with oil. Perhaps ignited by the steam-engine’s boiler, the well suddenly erupted into flames that engulfed Rouse, killing him and 18 others and seriously burning many more.
Historian Michael H. Scruggs of Pennsylvania State University found a dramatic account from an eyewitness, who reported:
“One of the victims it would seem had been standing on these barrels near the well when the explosion occurred; for I first discovered him running over them away from the well. He had hardly reached the outer edge of the field of fire, when coming to a vacant space in the tier of barrels from which two or three had been taken, he fell into the vacancy, and there uttering heart-rending shrieks, burned to death with scarcely a dozen feet of impassable heated air between him and his friends.”

Henry R. Rouse, 1823-1861.
Scruggs noted the 37-year-old Henry Rouse was dragged from the fire severely burned, and expecting the worst, dictated his Last Will and Testament, “to the men surrounding him as they fed him water spoonful by spoonful.”

Engraved on an 1865 marble monument (re-dedicated to Rouse’s memory during a family reunion in 1993) is this tribute:
Henry R. Rouse was the typical poor boy who grew rich through his own efforts and a little luck. He was in the oil business less than 19 months; he made his fortune from it and lost his life because of it. He died bravely, left his wealth wisely, and today is hardly remembered by posterity. — from the Rouse Estate.
The 1865 Atlas of the Oil Regions of Pennsylvania by Frederick W. Beers described this early petroleum industry tragedy in detail:
It was upon this farm (Buchanan) that the terrible calamity of April 1861, occurred, when several persons lost their lives by the burning of a well. The “BURNING WELL” as it has since been called, had been put down to the depth of three hundred and thirty feet, when a strong vein of gas and oil was struck, causing suspension of operations and ejecting a stream from the well as high as the top of the derrick.

“Atlas of the Oil Regions of Pennsylvania,” published by Frederick W. Beers in 1865.
Large numbers of persons were attracted to the scene, when the gas filling the atmosphere took fire, as is supposed, from a lighted cigar, and a terrible explosion ensued, which was heard for three or four miles. The well well continued to burn upwards of twenty hours destroying the tanks and machinery of several adjacent wells, and several hundred barrels of oil. The scene is represented as terrific beyond comparison.
The well spouted furiously for many hours, and the column of flame extended often two and three hundred feet in height, the valley being shut in, as it were, by a dense and impenetrable canopy of overhanging smoke. Fifteen persons were instantly killed by the explosion of the gas, and thirteen others scarred for life.

Among the persons killed was Mr. Henry R. Rouse, who had then recently become interested in that locality, and after whom Rouseville takes its name. The well continue to flow at the rate about one thousand barrels per day for a week after the fire, when it suddenly ceased, and has since produced very little oil as a pumping well.
These fires have not been unfrequent, and it is a little remarkable that in every case where wells have been so burned they have never after produced save in very small quantities.

Late 1860s stereograph by William J. Portser showing men and women standing on a storage tank and two men at the top of an oil derrick in Pennsylvania, courtesy Library of Congress.
According to historian Scruggs, the knowledge gained from the 1861 disaster along with other early oilfield accidents brought better exploration and production technologies. The first “Christmas Tree” — an assembly of control valves – was invented by Al Hamills after the 1901 gusher at Spindletop Hill, Texas.
Although the deadly Rouseville well fire cause devastation, “the knowledge gained from the well along with other accidents has help paved the way for new and safer ways to drill,” Scruggs wrote in his 2010 article.
“These inventions and precautions have become very important and helpful, especially considering many Pennsylvanians are back on the rigs again, this time drilling for the Marcellus Shale natural gas,” he concluded.
Learn more about another important invention, Harry Cameron’s 1922 blow out preventer in Ending Gushers – BOP.
Oil Well Fire at Night
The tragic Pennsylvania oil well fire was immortalized by Philadelphia artist James Hamilton, a mid-19th century painter whose landscape and maritime works are in collections of the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City, the Tate Gallery in London, and the Smithsonian American Art Museum (SAAM) in Washington, D.C.

Acquired by the Smithsonian American Art Museum in 2017, artist James Hamilton’s “Burning Oil Well at Night, near Rouseville, Pennsylvania,” was on display in 2018. Photo by Bruce Wells.
In 2017, the Smithsonian museum acquired Hamilton’s “Burning Oil Well at Night, near Rouseville, Pennsylvania,” circa 1861 (oil on paperboard, 22 inches by 16 1⁄8 inches, currently not on view).
“Rouseville, Pennsylvania, lay within a few miles of Titusville and Pithole City, two of the most famous boom towns in Pennsylvania ’s oil fields,” noted the museum’s 2017 description of the painting.

“From 1859 until after the Civil War, new gushers brought investors, cardsharps, saloons, and speculators into these rural settlements. As quickly as they grew, however, the towns collapsed, often from the effects of fires like the one shown here,” noted the Smithsonian’s description.
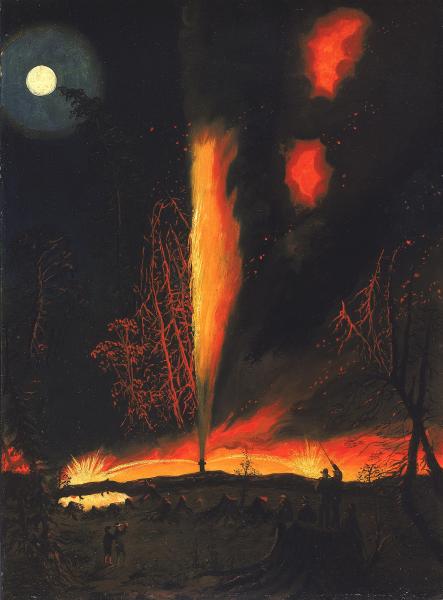

Flames shooting from the wellhead are part of the circa 1861 “Burning Oil Well at Night, near Rouseville, Pennsylvania,” by James Hamilton.
“In the 1860s, American industrialist John D. Rockefeller (1839-1937) was in the thick of this oil boom, maneuvering to establish the Standard Oil Company,” the museum’s painting description added. “Rockefeller’s investments in railroads and refineries would make him one of America’s richest men, long after the wildcatters in the Pennsylvania fields had gone bust.”
Famed journalist and Rockefeller antagonist Ida Tarbell lived in Rouseville as a child.
Following the Civil War, with consumers increasingly demanding kerosene for lamps (and soon gasoline for autos), the search for oilfields moved westward. The young petroleum industry also developed safety and accident prevention methods alongside new oilfield firefighting technologies.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Trek of the Oil Finders: A History of Exploration for Petroleum (1975); Atlas of the oil region of Pennsylvania (1984); Cherry Run Valley: Plumer, Pithole, and Oil City, Pennsylvania (2000); Warren County (2015). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
Citation Information: Article Title: “Fatal Oil Well Fire of 1861.” Authors: B.A. Wells and K.L. Wells. Website Name: American Oil & Gas Historical Society. URL: https://aoghs.org/petroleum-pioneers/first-oil-well-fire. Last Updated: April 10, 2024. Original Published Date: April 29, 2013.
by Bruce Wells | Mar 8, 2024 | Petroleum Art
How the red Pegasus soared into Dallas petroleum history.
The Mobil Oil Pegasus perched atop the Magnolia Petroleum building in Dallas from 1934 until 1999, when rust and growing structural issues forced its removal. On the first day of 2000, a carefully crafted duplicate returned to the Dallas skyline.
Thanks to its widespread popularity, Mobil Oil’s high-flying trademark returned to its Texas home with one red Pegasus on each side of a sign painstakingly recreated by the American Porcelain Enamel Company. As the year 1999 drew to a close, the duplicated red Pegasus soared again.

The rotating 35-foot by 40-foot Pegasus sign first beamed its red neon glow above a Dallas hotel in 1934.
A Dallas hotel would later restore the original Mobil Oil Pegasus after finding its rusted remains in a city-owned shed. The Omni Dallas Hotel funded the restoration, and in 2015 the surviving red neon-edged symbol — a one-sided version — was re-lit in front of the Omni on Lamar Street.
The Mobil Oil (now ExxonMobil) trademark has been a feature of Dallas since first welcoming attendees to a 1934 convention of petroleum company executives.

The Magnolia building’s red Pegasus has remained one of the most recognizable corporate symbols in American history, and a marketing rival of the Sinclair dinosaur.
Magnolia Petroleum
When the 400-foot-tall Magnolia Petroleum building opened in 1922, it was the city’s first skyscraper — and tallest building west of the Mississippi River. With 29 floors and seven elevators, the Magnolia building towered over the nearby Adolphus Hotel, built in 1913.
The Magnolia building’s multimillion dollar construction featured a “modified classical design” by a well known architect from the United Kingdom. The Texas Historic Historical Commission in 1978 placed a marker at Commerce and Akard streets noting:
Erected in 1921-22, this building housed the offices of Magnolia Petroleum Co., later Mobil Oil Co. It was designed by Sir Alfred C. Bossom (1881-1965), noted British architect, and built at a cost of $4 million. The tallest structure in Dallas for almost 20 years, it reflected the city’s increasing economic importance. In 1934 a revolving neon sign was placed atop the building. The “Flying Red Horse,” trademark for Magnolia products, quickly became a local landmark.
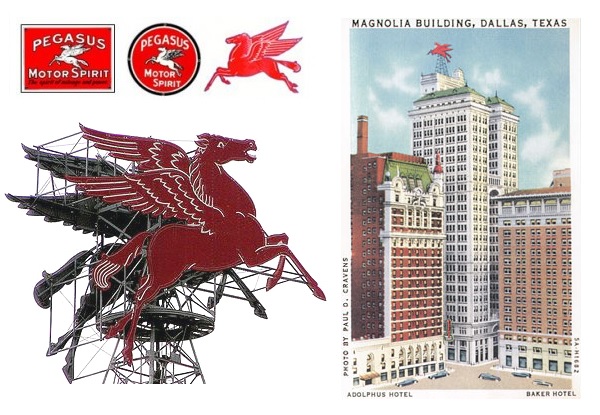
Vacuum Oil Company trademarked the Pegasus logo in 1911 and by the 1930s was marketing Pegasus Motor Spirits and Mobiloil. The Magnolia Petroleum building, completed in 1922, was “a great peg driven into the ground holding Dallas in its place.” Pegasus landed atop the building in 1934 — in time for the first annual meeting of the American Petroleum Institute.
The Magnolia building also was the first high-rise in the United States to have air conditioning, according to the management company that acquired it in 1997. A fully restored lobby features a gold leaf decorative plaster and original elevator doors engraved with the Pegasus logo.

Much of the original architecture’s classical design has been restored, according to the Magnolia Dallas Downtown — a boutique hotel blending the historic building’s past with modern amenities.

An 11-foot Mobil Oil Pegasus displayed at the 1939 New York World’s Fair found its way to a Mobil service station in Casa Linda, Texas, and later to a Dallas County museum.
After the Magnolia building’s 1922 opening, a local reporter described the oil company headquarters building as “a great peg driven into the ground holding Dallas in its place.”

A circa 1935 Dallas skyline postcard given to visitors to the observatory tower in the Magnolia Building. Image courtesy DeGolyer Library, Southern Methodist University, digital collection.
When Standard Oil Company of New York (Socony) acquired the Magnolia Petroleum Company in 1925, the building was part of the deal. Nine years later, the two-sided Pegasus sign would land on its roof.
Pegasus takes Flight
The Mobil Oil Pegasus began its journey in 1911, when a Vacuum Oil Company subsidiary in Cape Town, South Africa, first trademarked the Pegasus logo. Based in Rochester, New York, Vacuum Oil had built a successful petroleum lubricants business around an 1869 patent by its founder, Hiram Everest, long before gasoline was even a branded product.

Vacuum Oil Company’s products used a gargoyle prior to adopting the winged horse of mythology.
At first, a stylized red gargoyle advertised the company, which produced early petroleum-based lubricants for horse-drawn carriages and steam engines. The Pegasus trademark proved to be a more enduring image. In Greek mythology, Pegasus – a winged horse – carried thunderbolts for Zeus.

By 1931, growth of the automobile industry expanded the Vacuum Oil product lineup to include Pegasus Spirits and Mobilgas – later simplified to Mobil. When Standard Oil of New York and Vacuum Oil combined to form Socony-Vacuum Oil Company, the new company adopted the familiar winged trademark, as did an affiliate, Magnolia Petroleum.

The certificate from Cape Town, South Africa, notes that the “Vacuum Oil Company of South Africa Limited” is named “as proprietor of the Trade Mark represented above.” Image courtesy ExxonMobil Historical Collection/Center for American History, University of Texas, Austin.
It took a year to build the rotating 35-foot by 40-foot Pegasus sign, which beamed a red neon glow in 1934 to welcome the first annual meeting to be held in Dallas by the American Petroleum Institute (API). For decades the emblem slowly rotated above the growing city as corporate consolidations and mergers changed Socony-Vacuum ownership.
In 1955, the name of the company changed to Socony Mobil Oil; in 1966 became just Mobil Oil. A neon Mobil Oil Pegasus displayed at the 1939 New York World’s Fair found its way to a Mobil gas station in Casa Linda, Texas, and later to the Old Red Museum of Dallas County History & Culture. The museum was closed by 2024, when its historic building — the original Dallas County Courthouse — became home to the Texas Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals.
A New Pegasus
In 1974 the petroleum icon’s motor ground to a halt. Mobile Oil moved out of the Magnolia building three years later and sold the aging skyscraper and glowing but unmoving sign to the city of Dallas. Twenty-years later, Pegasus’ neon lights finally went out.

As a Denver-based developer restored and transformed the deteriorating Magnolia building into a luxurious 330 room hotel in the late 1990s, a group of patrons and corporate partners joined in to bring the broken and rusty Pegasus sign back to life. They raised more than $600,000 for the project.
The Project Pegasus team targeted New Year’s Eve of 1999 to reintroduce Dallas citizens to their petroleum heritage landmark. Restoration of the 8,000-pound sign proved challenging.
The derrick-like tower structure was reparable and the old mechanical rotation system could be updated with new technology.

A view of Pegasus in photographer Carolyn Brown’s 2004 book, Dallas: Where Dreams Come True.
But time and weather had damaged the porcelain coated steel signage and neon tubing. New 16-gauge steel panels had to be cut, using the originals as templates.
Only two facilities in the United States were large enough to accommodate baking the emblematic red porcelain onto the new panels; fortunately, both were in Dallas. More than 1,000 feet of new neon tubing was required to trace the familiar outlines as craftsmen and technicians remained faithful to the original.
The Red Icon Returns
Oil history preservation efforts were rewarded at midnight on December 31, 1999, when new millennium celebrations welcomed the red Mobil Oil Pegasus back to the Dallas skyline.
“You can’t tell the new one from the old one except for the fact that the faces are now red and not rusty,” explained one of the restorers. “We replaced every old piece with a new piece that was exactly the same as it was before.”

The Pegasus sign “is a beloved icon of the city of Dallas,” proclaimed Kay Kallos, public art manager in the Office of Cultural Affairs, which manages its maintenance. Mobil Oil merged with Exxon in 1999, creating ExxonMobil, headquartered in Irving, Texas.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Become an AOGHS annual supporting member and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
Citation Information – Article Title: “Mobil’s High-Flying Trademark.” Authors: B.A. Wells and K.L. Wells. Website Name: American Oil & Gas Historical Society. URL: https://aoghs.org/petroleum-art/high-flying-trademark. Last Updated: March 11, 2024. Original Published Date: March 14, 2010.
by Bruce Wells | Feb 13, 2024 | Petroleum Art
Artist Bob “Daddy-O” Wade used petroleum pipelines to create a towering Texas landmark.
With more than 2.5 million miles of oil and natural gas pipelines crisscrossing the United States, an offbeat Texas sculptor in 1993 repurposed about 70 feet to create a work of art.
Most Texas travelers at some point have seen the monumental sculptures of Bob “Daddy-O” Wade, known for “keeping it weird” since making the Austin scene in 1961. The decades of artworks by “Daddy-O” have reflected his unusual Texas sense of scale, according to Texas A&M University Press. (more…)
by Bruce Wells | Jan 3, 2024 | Petroleum Art
Dr. Seuss created zoological oddities for Esso products of Standard Oil Company of New Jersey.
Seuss the oilman? Thirty years before the Grinch stole Christmas in 1957, many strange and wonderful critters of the popular children’s book author could be seen in Standard Oil Company advertising campaigns.

Between 1930 and 1940, Theodor Seuss Geisel created distinctive characters for Standard Oil advertising campaigns, including this “wise bird” for Essolube oil change cards. Illustration courtesy University of California San Diego Library.
During the Great Depression, fanciful creatures drawn by the future Dr. Seuss promoted Essolube and other products for Standard Oil of New Jersey. He later said his experience at Standard, “taught me conciseness and how to marry pictures with words.”

A 1927 cartoon by Theodor Seuss Geisel featured Standard Oil’s petroleum product “Flit,” a popular bug spray.
In the cartoon that launched his career, Theodor Seuss Geisel drew a peculiar dragon inside a castle. The January 14, 1928, issue of New York City’s Judge magazine featured the beast. Geisel would soon introduce America to many less threatening characters inhabiting his imaginative menagerie.
“Flit,” was a popular bug spray of the day — especially against flies and mosquitoes. It was one of many Standard Oil Company of New Jersey consumer products derived from oil and natural gas (also see petroleum products).

Late in 1927, Standard Oil’s growing advertising department, which had focused on sales of Standard and Esso gasoline, lubricating oil, fuel oil and asphalt, reorganized to promote other products, according to author Alfred Chandler Jr.

Dr. Seuss later said his experience working at Standard Oil helped him develop his fantastical characters and tales.
“Specialties, such as Nujol, Flit, Mistol, and other petroleum by-products that could not be effectively sold through the department’s sales organization were combined in a separate subsidiary — Stanco,” noted Chandler in his book, Strategy and Structure: Chapters in the History of the American Industrial Enterprise.
Chandler’s 1962 book also examined General Motors Company, Sears, Roebuck and Company, and gunpowder manufacturer E.I. du Pont de Nemours.
“Quick, Henry, the Flit!”
Geisel’s fortuitous bug-spray cartoon depicted a medieval knight in his bed, facing a dragon who had invaded his room, and lamenting, “Darn it all, another dragon. And just after I’d sprayed the whole castle with Flit.”

According to nn anecdote in Judith and Neil Morgan’s 1995 book Dr. Seuss and Mrs. Geisel, the wife of the advertising executive who handled the Standard Oil account was impressed by the cartoon.

Circa 1935 ad for a Standard Oil petroleum product was characteristic of the imagination that would make Ted Geisel the definitive children’s book author. Illustration courtesy University of California San Diego Library.
“At her urging, her husband hired the artist, thereby inaugurating a 17-year campaign of ads whose recurring plea, ‘Quick, Henry, the Flit!,’ became a common catchphrase,” noted a curator of the Dr. Seuss Collection at the University of California, San Diego.
“These ads, along with those for several other companies, supported the Geisels throughout the Great Depression and the nascent period of his writing career,” the curator added.
Besides promoting the Standard Oil companies Flit and Esso, Dr. Seuss’ creations helped sell such diverse goods as ball bearings, radio programs, beer brands, and sugar, notes the library, located in La Jolla, where Geisel was a longtime resident.

This 1932 Standard Oil Company (New Jersey) advertisement is among those preserved by the Dr. Seuss Collection of the Mandeville Special Collections Library at the University of California, San Diego.
At the University of California, San Diego, the Dr. Seuss Collection in the Mandeville Special Collections Library contains original drawings, sketches, proofs, notebooks, manuscript drafts, books, audio and videotapes, photographs, and memorabilia.

More than 8,500 items document and preserve Dr. Seuss’ creative achievements, beginning in 1919 with his high school activities and ending with his death in 1991.
Karbo-nockus and Other Critters
The future Dr. Seuss added a host of zoological oddities to Standard Oil’s lexicon while promoting Esso products (Esso was an acronym for Eastern States Standard Oil). His critters promoted Essomarine oil and greases as well as Essolube Five-Star Motor Oil.

Standard Oil advertising campaigns provided a steady income to Geisel and his wife throughout his early days experimenting with his drawings.
Smiling, toothy creatures such as Zero-doccus, Karbo-nockus, Moto-raspus and Oilio-Gobelus appeared in advertisements that warned motorists of the hazards of driving without the protection of Standard Oil lubrication.

Motor oil cartoon ad drawn by the future children’s book author Dr. Seuss. First sold in the 1930s, Essolube has remained a popular product, today for ExxonMobil.
“Meet the Zero-doccus. He is the first if a group of terrible beasts that are being turned loose in the advertising of Essolube, Standard Oil Company (New Jersey) products,” reported the December 8, 1932, Printers’ Insider, an advertising trade journal.
Other Esso “moto-monsters” would be introduced in newspapers and outdoor posters in coming months, the trade journal proclaimed.
“These creatures symbolize and dramatize some of the troubles of motorists who use inferior oils. The Zero-doccus pounces on cold motors and makes quick starting difficult with ordinary oils,” the article noted. “He and his coming friends are the creations of Dr. Seuss of ‘Quick, Henry, the Flit’ fame.”
The Printers’ Insider article predicted the strange Esso creatures would prove popular when they appeared in ads nationwide.

A dependable income from Standard Oil during the Great Depression helped Dr. Seuss publish his first children’s book in 1936.
Seuss in Esso Navy
Throughout his early hard years, these Standard Oil advertising campaigns provided steady income to Geisel and his wife. “It wasn’t the greatest pay, but it covered my overhead so I could experiment with my drawings,” he later said.
Geisel noted his advertising work allowed him to experiment creating subtle visual messages while using wacky rhymes in story telling.

In 1936, Geisel designed Standard Oil’s Essomarine booth for the National Motorboat Show — and created the phenomenally successful “Seuss Navy.” Young and old visitors were commissioned as admirals and photographed with whimsical characters made of cardboard.

Standard Oil Company marketers promoted Essomarine products during the 1940 National Motor Boat Show in New York City.
By 1940, the Seuss Navy included more than 2,000 enthusiastic admirals (with such notables as bandleader Guy Lombardo). Geisel remembered that, “It was cheaper to give a party for a few thousand people, furnishing all the booze, than it was to advertise in full-page ads.”
As Dr. Seuss, Geisel wrote and illustrated his first children’s book, And to Think That I Saw It on Mulberry Street, published on December 21, 1937, by Vanguard Press after being rejected by 27 other publishers.
Twenty years later, The Cat in the Hat was inspired by a 1954 Life Magazine essay critical of children’s literacy and the stilted “See Spot Run” style of reading primers. Published in 1957, The Cat in the Hat used just 236 words — and only 14 of them with two syllables. It remains his most popular work.
The former Standard Oil advertising illustrator wrote more than 50 children’s books over a half-century career that brought the world Hop on Pop, Green Eggs and Ham and many others. Children lost a friend on September 24, 1991, when Theodor Seuss Geisel died at the age of 87.
View online the Dr. Seuss Collection: Advertising Artwork of Dr. Seuss, preserved by Mandeville Special Collections Library, University of California.
Kerosene in Art
At the beginning of the 20th century, French illustrator Jules Chéret (1836-1933) was famous for his lithograph posters for theatres, music halls, beverages, and medicines. During a long career, many of his commercial posters promoted a French petroleum company’s lamp oil.

Chéret, who would be called “the father of the modern lithograph” and “king of the poster,” produced popular posters for “Saxoleinem,” the company’s refined “pétole de sureté”– safety lamp oil.

French advertisement for “The Halo of the South,” a safety oil for lamps, in an 1895-1900 lithograph by artist Jules Chéret.
“He was often imitated, and an entire generation of artists would follow and build on his work. One of them was Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec,” notes Chicago’s Richard H. Driehaus Museum. “To acknowledge his debt to the older artist, Lautrec sent Chéret a copy of every poster he produced.”
Learn about more examples of artists and the petroleum industry in Oil in Art.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Theodor Geisel: A Portrait of the Man Who Became Dr. Seuss (2010); The History of the Standard Oil Company: All Volumes
(2010); The History of the Standard Oil Company: All Volumes  (2015); Strategy and Structure: Chapters in the History of the American Industrial Enterprise (1962); Dr. Seuss & Mr. Geisel: A Biography (1995). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2015); Strategy and Structure: Chapters in the History of the American Industrial Enterprise (1962); Dr. Seuss & Mr. Geisel: A Biography (1995). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Become an AOGHS annual supporting member and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
Citation Information – Article Title: “Seuss I am, an Oilman.” Authors: B.A. Wells and K.L. Wells. Website Name: American Oil & Gas Historical Society. URL: https://aoghs.org/petroleum-art/seuss-the-oilman. Last Updated: January 4, 2024. Original Published Date: December 1, 2008.
by Bruce Wells | Dec 16, 2023 | Petroleum Art
Cartographer visited petroleum boom towns to draw popular bird’s-eye views.
Thaddeus M. Fowler created detailed, panoramic maps of America’s earliest petroleum boom towns during the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. His popular cartographic depictions of oil patch communities in Pennsylvania, Oklahoma, and Texas offered “aero views” seemingly drawn from great heights.
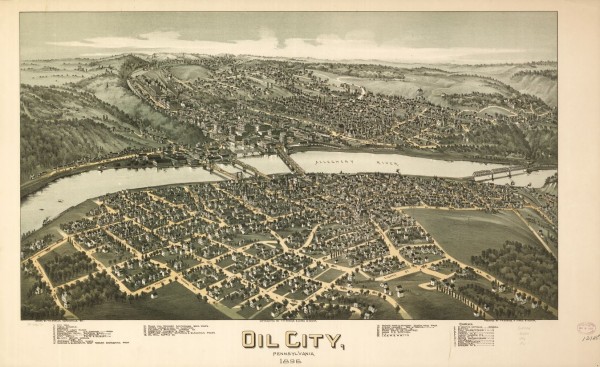
More than 400 Thaddeus Fowler panoramas have been identified. There are 324 in the Library of Congress, including this one of Oil City, Pennsylvania, in 1896. Source: Library of Congress Geography and Map Division, Washington, D.C.
Fowler has the largest number of panoramic maps in the collection of the Library of Congress (LOC) in Washington, D.C. His hand-drawn lithographs have fascinated viewers since the Victorian Age. Being depicted in one of Fowler’s maps, also known as “bird’s-eye views,” was a matter of civic pride for many community leaders. (more…)
by Bruce Wells | Oct 31, 2023 | Petroleum Art
The use of energy resources has defined modern civilization. Museums, and historians, writers, and educators have preserved the heritage of the petroleum industry since the first U.S. well of 1859. Oilfield artists of all media remain important recorders and interpreters of petroleum’s worldwide influence.
For oil patch students and researchers, the American Oil & Gas Historical Society created the work-in-progress Oil in Art articles, to accompany the forums and resources page, which includes links for photography sources (especially universities and the Library of Congress), petroleum history videos, and a small AOGHS selection of books and authors.
(more…)




























